What is Medical Weight Loss?
When a person loses weight, the body responds by increasing hunger signals, decreasing satiety (fullness) signals, and slowing the metabolism. This makes continuing to lose weight and sustaining weight loss quite difficult. Medical weight loss is when a doctor uses medication to offset these metabolic adaptations.
What kinds of medications are used for medical weight loss?
Several old medications including Phentermine and Diethylpropion (Tenuate) are still in use today. These medications are inexpensive and very effective. They work by reducing appetite, therefore offsetting the natural increase in appetite that happens with weight loss. They are mild stimulants, so people often have improved focus and energy. However, if too strong, they can make a person anxious, increase heart rate or blood pressure, or cause insomnia. However, for most individuals, side effects are mild and pass in a few days. We generally avoid these medications in people with difficult to control blood pressure or pre-existing heart conditions.
There are also a variety of new weight loss medications available.
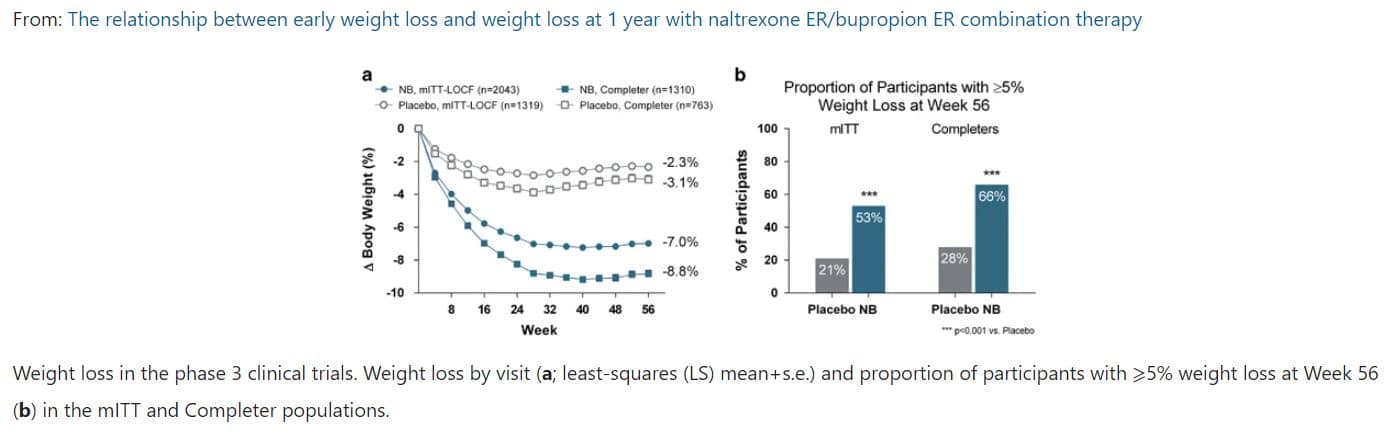
Contrave is a combination of bupropion and naltrexone. It works in two areas of the brain to control hunger and cravings. It is not considered a stimulant. Side effects can include nausea, constipation, headaches and insomnia. It should not be used in people with a seizure history or high seizure risk.
Qsymia is a new version of phentermine. In addition to the phentermine, there is topiramate in each pill, which kicks in later in the day to help control hunger during the evening hours. It is important not to become pregnant on Qsymia, as it is possible for topiramate to cause birth defects including cleft palate.
Saxenda is a once daily injectable medication that works through a hormonal mechanism that signals the brain that it is in a fed state. This is an analogue of a hormone that the small intestine naturally makes in response to eating called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1). These medications have long been used as safe, effective options for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Saxenda contains the same active ingredient as Victoza, which is used for diabetes. It should not be used in people with a rare form of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (or people with a family history of this), multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, or pancreatitis. Side effects can include nausea, vomiting and other gastrointestinal problems, but generally are mild and fade as a person gets used to the medication. It is quite expensive, so if you are interested in using Saxenda as your medical weight loss tool, be sure to check with your insurance carrier.
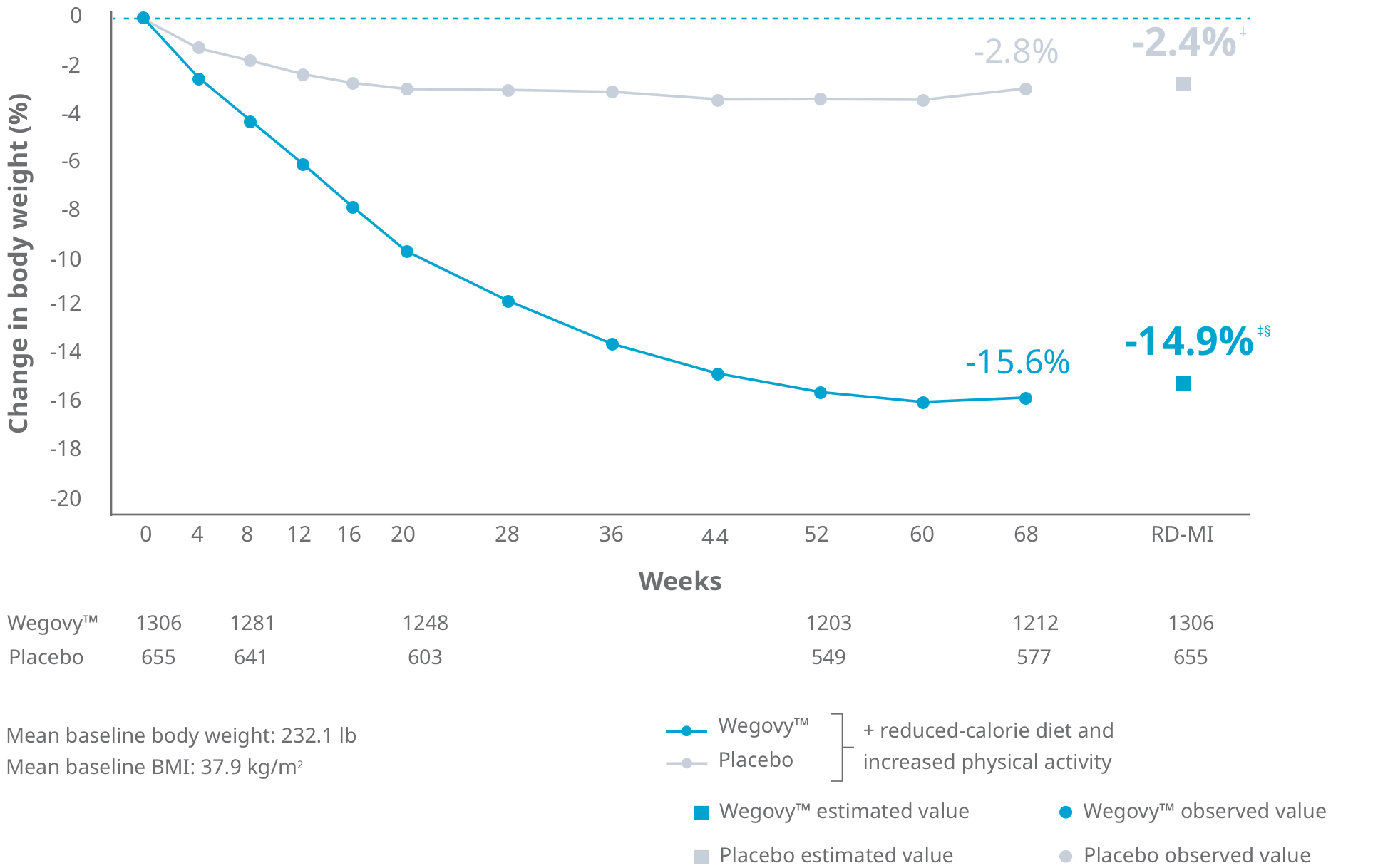
Wegovy is a once weekly injectable medication that works similarly to the Saxenda, above. It has a much longer half-life, so it is injected just once per week. Wegovy provides much more weight loss on average than the other options including Saxenda. The side effects and warnings are similar to Saxenda (above).
Beyond Weight Loss Medications
Most people with obesity are on medications for a variety of obesity-related conditions ranging from diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, depression, insomnia, hypothyroidism and countless others. Unfortunately, many of these medications can contribute to weight gain and/or make weight loss difficult. The heart of medical weight loss is when in addition to using weight loss medications, oftentimes the obesity medicine physician can stop medications that may become unnecessary with weight loss, or alternatively substitute a weight-neutral medication (or sometimes one that can actually help with weight loss.) We will work with you individually to optimize as much as we can to help you lose the weight and keep it off.




